Lipoma Causes Symptoms and Treatment
Lipoma is a common and non-cancerous growth of fat cells that can develop under the skin. It is estimated that up to 2% of the population may have lipomas, making it a prevalent condition. Despite its benign nature, it is essential to address lipoma to avoid potential complications and discomfort. The aim of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of lipoma, from its causes to prevention methods. By the end of this article, readers will have a better understanding of lipoma and how to manage it effectively.
What is Lipoma?
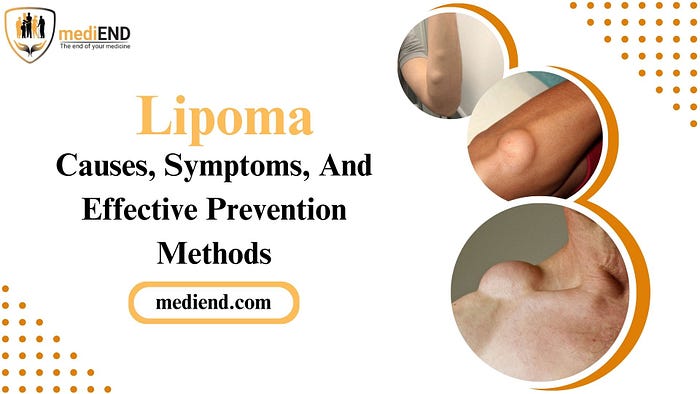
Lipoma is a common benign tumor that forms under the skin. It is composed of fat cells and can occur in any part of the body, but is most commonly found on the neck, shoulders, arms, and torso. Lipomas are non-cancerous and do not usually cause any harm, but they can be concerning due to their appearance and potential growth. There are different types of lipomas, such as superficial and deep-seated, which may vary in size and location. Lipomas are prevalent in the population, with about 1 in 100 people having them. Despite being harmless, addressing lipoma is important for overall health and wellness. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive understanding of lipoma, covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and effective prevention methods.
Symptoms of Lipoma
· Lipoma typically presents as a soft, painless lump under the skin.
· It is commonly found on the neck, shoulders, back, arms, and thighs.
· The size of lipoma can range from small pea-sized to large grapefruit-sized.
· In rare cases, lipoma may cause pressure or discomfort if it grows near nerves or organs.
· Some people may experience multiple lipomas on their body.
It is important to note that lipoma symptoms may vary depending on the location and size of the lump. For example, a lipoma on the neck may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing, while a lipoma on the thigh may cause discomfort when walking or sitting for long periods.
Understanding Gynecomastia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is recommended to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis. In some cases, a lipoma may also be a sign of an underlying condition such as familial multiple lipomatosis or Gardner’s syndrome.
Early detection and diagnosis of lipoma can help prevent any potential complications and ensure appropriate treatment. Next, let’s take a look at the potential causes of lipoma and how it can be diagnosed.
Causes of Lipoma
There is no definitive answer to what causes lipoma, but research suggests that there may be a combination of genetic and environmental factors at play. Lipoma is more commonly seen in people with a family history of the condition. Hormonal imbalances and advancing age have also been linked to the development of lipoma.
Furthermore, certain underlying conditions such as adiposis dolorosa, Gardner syndrome, and Cowden syndrome have been associated with an increased risk of developing lipoma. It is important to note that these conditions are rare and not all individuals with lipoma will have an underlying condition.
While the exact cause of lipoma may not be known, it is important to monitor any suspicious lumps on the body and seek medical attention for proper Diagnosis and Treatment. Early detection and management can help prevent further growth and potential complications of lipoma.
Diagnosis of Lipoma
Lipoma is typically diagnosed through a physical examination by a doctor or dermatologist. They will assess the location, size, and appearance of the lump to determine if it is a lipoma. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
It is important to seek a professional diagnosis for any suspicious lumps on the body, as lipoma can be mistaken for other skin conditions. Early detection and accurate diagnosis can help determine the best course of treatment and prevent any potential complications.
Differentiating Lipoma from Other Skin Conditions
Lipoma can often be differentiated from other skin conditions such as cysts, fibromas, or liposarcoma based on its characteristic features. Lipoma is usually soft to the touch, moves easily under the skin, and has a doughy texture.
It is important to consult with a doctor for a proper diagnosis and to rule out any other underlying conditions that may be causing the lump.
Treatment Options for Lipoma
There are various treatment options available for individuals with lipoma. The type of treatment recommended will depend on the size and location of the lipoma, as well as the individual’s personal preferences. Some of the treatment options include:
1. Observation: In many cases, lipomas are harmless and do not require any treatment. Your doctor may recommend monitoring the lipoma over time to see if it changes in size or causes any discomfort.
2. Steroid Injections: For smaller lipomas, steroid injections may be used to help shrink the lump. This treatment is typically used for cosmetic reasons or if the lipoma is causing discomfort.
3. Liposuction: This is a minimally invasive procedure where a thin tube is inserted into the lipoma and used to suction out the fatty tissue. This is often used for larger, more visible lipomas.
4. Surgical Removal: In cases where the lipoma is causing discomfort or is located in an area that affects daily activities, surgical removal may be recommended. This involves making a small incision and removing the lipoma.
It’s important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of each treatment option with your doctor to determine the best course of action for your specific case. Early detection and prompt treatment can help prevent complications and ensure the best possible outcome.
When to Call a Doctor
If you notice a lump or swelling on your body, it’s important to have a doctor examine it. They can determine whether it’s a benign lipoma or if further tests are necessary. For information on treatment options for lipomas, you can visit our webpage. While lipomas can occasionally develop within muscles or internal organs, it’s uncommon. If a lipoma is causing discomfort or impacting muscle function, surgical removal might be required. Although rare, a lump could indicate a liposarcoma, a type of cancer that grows quickly and may cause pain. If your doctor suspects this condition, additional tests will be recommended.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lipoma is a common and often harmless condition, but it is important to understand its causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options. It is crucial to seek medical attention if you notice any suspicious lumps on your body and to follow through with a proper diagnosis. With a better understanding of lipoma, you can take proactive steps in preventing it and maintaining your overall health and wellness. Remember to consult with your doctor for the best treatment plan for your individual case. Stay informed and take care of your body to live a healthy life. Don’t ignore any abnormal changes in your body and seek medical advice to address them effectively. Together, we can work towards preventing and managing lipoma for a better quality of life.
Comments
Post a Comment